RESEARCH ARTICLE
MOTS-C: The “Centenarian” Peptide for Metabolic Enhancement and Longevity
Introduction:
What’s the difference between those who live to 100 and beyond, and those who find their lifespan cut short? One difference is a special peptide most people have never heard about – MOTS-C.
MOTS-C is a peptide with the power to extend lifespan while enhancing health, vitality, and quality of life, just like the centenarians in the world’s Blue Zones.
However, a significant problem with publicly available information regarding MOTS-C is that most of it appears to be based on outdated science at best, and completely inaccurate science at worst. Because of this, many people never realize its full potential.
But here’s what you need to know: MOTS-C is a peptide that's already inside you, actively working to regulate metabolism, endurance, and cellular health. The problem is that its levels decline with age. That’s why centenarians have higher levels, and why optimizing yours could help you to live longer.
In this article, you will learn what MOTS-C is, the science that is often overlooked by other experts, and how to determine the optimal dose to unlock its full potential for health and longevity. Lastly, I will share with you a secret peptide that can work orally to increase your mitochondria production of MOTS C. This is perfect for those who don’t want to use injection but still get some of the benefits of higher MOTS C levels.
What Is MOTS-C?
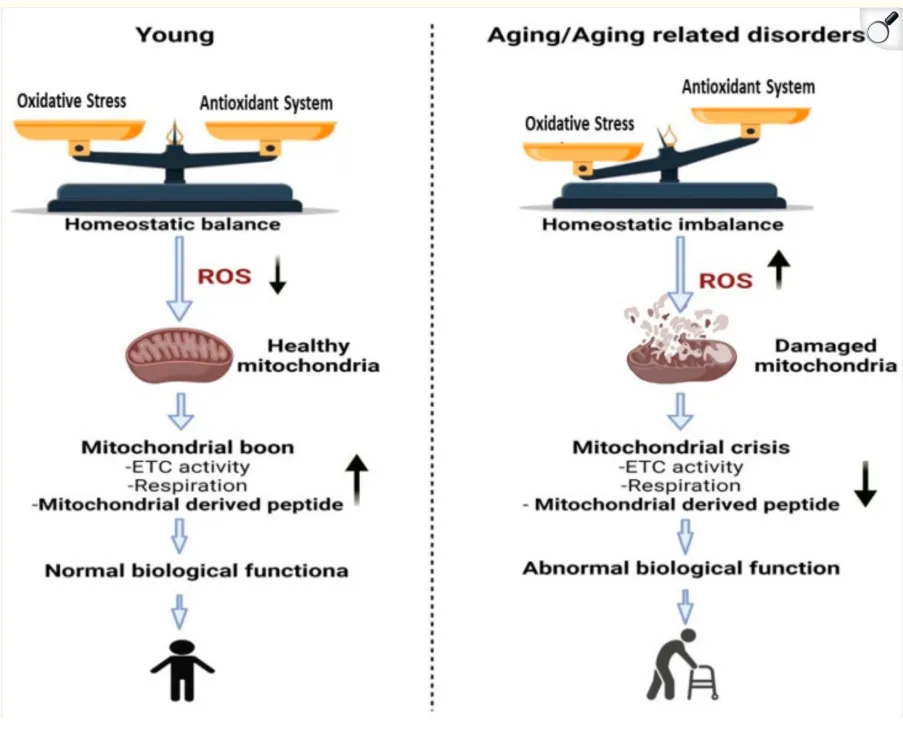
Mots C is a mitochondrial derived peptide encoded by mitochondrial DNA. It is transcribed in response to increased mitochondrial demands, such as during endurance exercise. Through its activation of the AICAR-AMPK pathway¹ and stimulation of mitochondrial biogenesis via PGC-1α², MOTS-C enhances mitochondrial function and improves glucose metabolism and metabolic health through downstream mediators Irisin and PPARa³ ⁴ expression that enhance insulin sensitivity and vascular health.
MOTS-C also facilitates the production of the vital coenzyme NAD+, which further supports metabolic health and cellular energy regulation⁵.
MOTS-C contributes to slowing down aging by promoting mitochondrial health, which is one intervention established to prevent the repression of genes associated with increased heterochromatin formation which occurs with aging⁶.
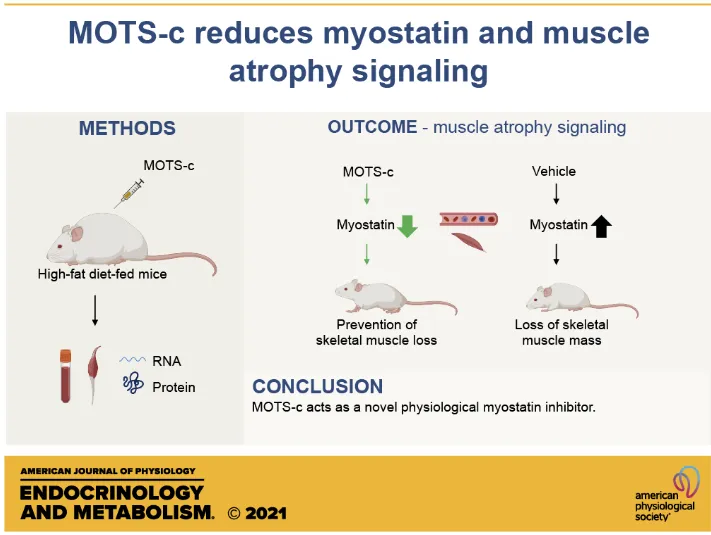
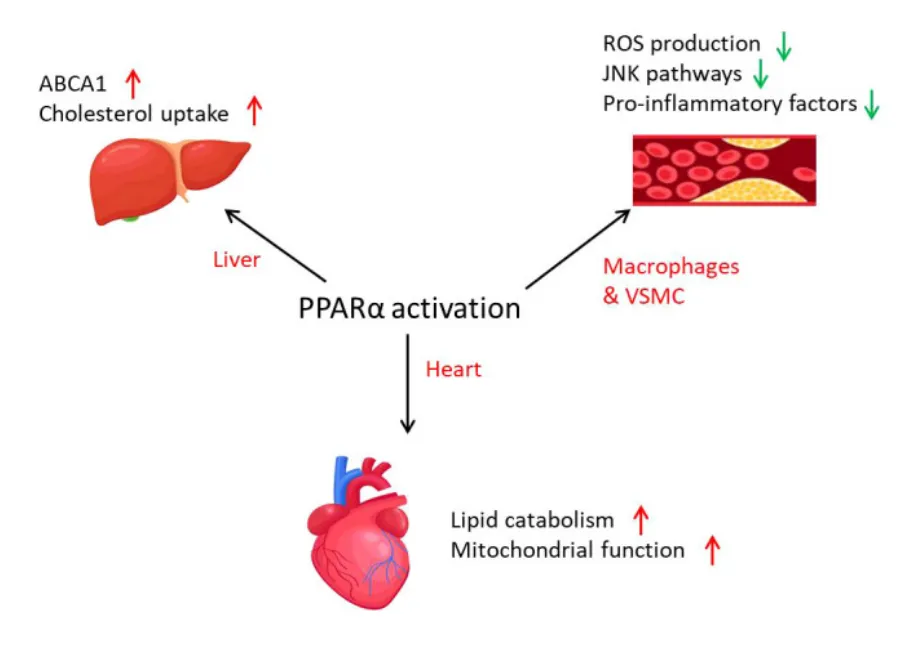
Cardiovascular Benefits:
Activates PPARa downstream from PGC1a for anti-inflammatory effects, improved lipid profiles, and cardioprotection¹⁰.

Because the benefits of Epitalon and Epithalamin often overlap and some of the largest human studies were conducted with Epithalamin, I will explore both in separate sections to provide a comprehensive perspective.
We know this because we are at the forefront of genetic analysis, and we’ve developed our own service “Precision Genomic Risk Prevention & Enhancement” which allows us to analyze and optimize genetic factors for our private coaching clients.
Calculating the Perfect MOTS-C Dose
If you search online, you’ll see the same generic dosage, usually 5mg, repeated everywhere. But where do these recommendations come from, and are they scientifically justified?
When I analyzed the available data, I calculated the ideal dose for MOTS-C using rigorous Human Equivalent Dose formulas. My findings showed that for a 70kg person, the optimal range spans 28mg-85mg for enhancing athletic performance or addressing vascular calcification, and around 5.67mg for improving diabetes when combined with exercise.
Here’s the issue:
While MOTS-C is naturally produced by the body, declines with age, and demonstrates significant benefits in rodent studies¹⁶, there have been no trials to establish an ideal human dose.
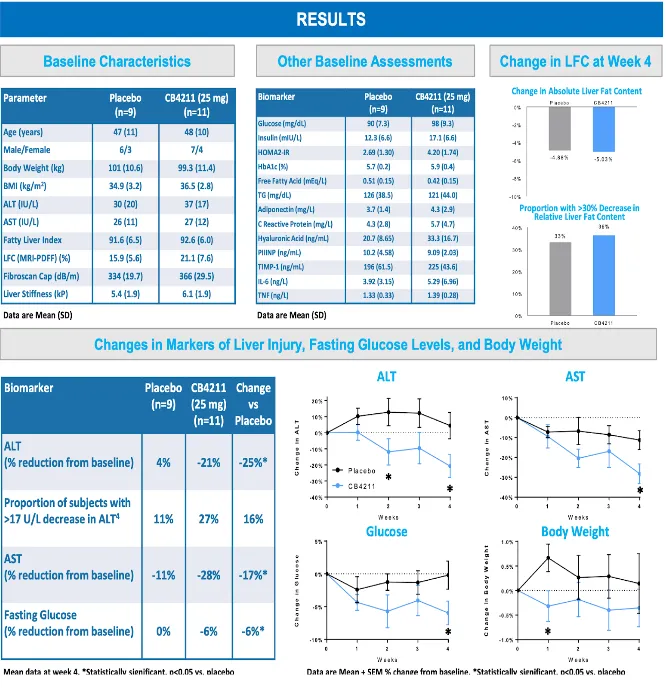
What we do have is a human trial for CB4211, a MOTS-C analog. This analog showed excellent results in improving Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and diabetes in obese patients when administered at 25mg daily injections for four weeks¹⁷.
So, we’re left with two options:
Stick with the generic recommendations repeated online.
Dive into the available science to calculate an equivalent human dose, which is precisely what I did.
Using Rodent Studies to Inform Dosage
To refine my recommendations, I analyzed several rodent studies on MOTS-C, each providing valuable insights into its dosing and effects:
•5mg/kg–15mg/kg improved exercise performance in mice, with the higher dose yielding better results specifically in older age¹⁸.
•5mg/kg enhanced vascular calcification reversal in rats¹⁹.
•0.5mg/kg improved diabetes outcomes in rats when combined with daily exercise for eight weeks²⁰.
To translate these findings into human applications, I utilized the Human Equivalent Dose formula, which accounts for species-specific differences in body surface area and drug metabolism²¹:
HED = (Animal Dose/kg) × (Animal Km / Human Km)
Calculated Human Doses for MOTS-C:
•Exercise Performance (15mg/kg mouse dose) = 1.215mg/kg for humans.
•Exercise Performance (5mg/kg mouse dose) = 0.405mg/kg for humans.
•Vascular Calcification (5mg/kg rat dose) = 0.81mg/kg for humans.
•Diabetes + Exercise (0.5mg/kg rat dose) = 0.081mg/kg for humans.
For a 70kg person, these calculations translate to a range of 5.67mg–85.05mg, depending on the desired outcome.
Conclusion:
The often-recommended 5mg dose may suffice for individuals with good metabolic health or those combining MOTS-C with exercise. However, it falls short for addressing more complex conditions like vascular calcification or for achieving peak athletic performance, especially in older individuals.
These conservative recommendations likely stem from the high cost of MOTS-C, prioritizing affordability over efficacy. But we should aim to present optimal dosages, so that those who can afford to invest in their health can unlock the peptide's full potential.
For those seeking a more affordable way to increase mitochondrial efficiency and endogenous MOTS-C production, or for those who prefer to avoid injections, consider Pinealon, a small tripeptide that may enhance MOTS-C levels through its unique mechanism.
Brenden Henry
February 20th 2025
About The Author:
Do you know the truth about peptides? We believe human beings deserve to live happy, healthy and pain-free. To help you do that, we turned our $997 peptide mastercourse into the biggest, most comprehensive and most important book on peptides ever written. And we’re giving it away FREE HERE:
This is our gift to you. We want to help you live a BETTER, HEALTHIER and HAPPIER life! This book will help you cut through the noise, get answers to your questions and teach you more about peptides than you’d learn in a $52,000 biology degree. It’s written by Brenden Henry, the world’s number one authority on peptide science, Dr. Ali Mazloum and Dan Fox. You can get your free physical copy right now from the link above!
Do you have health issues you haven’t managed to solve, concerns about your body declining or a desire to experience the highest levels of biological optimization? You should know about the life-changing results we create with our peptide transformation programs. Brenden Henry, Dr. Ali, and our team of specialists are some of the most advanced biohackers on Planet Earth. We can help you achieve almost ANYTHING you want when it comes to your brain and body. Take the next step here:
https://peptides.link/transformation
Want our most trusted & recommended peptide store? Go here:
https://peptides.link/vitastream
(use code CHANGEAGE10 for 10% off. They’re great quality, they have great service, they’re great people and they sell peptides made in the USA with 50% more ingredients than others!)
Do you want the FULL step-by-step roadmap to heal, enhance and transform your biology with peptides? This is the most comprehensive, complete, advanced, valuable and useful peptide class on Planet Earth (absolutely nothing else comes close). If you’d like to check this out, go here:
Want to discover exactly what peptides are capable of and how they’re so life-changing yet so unknown? Get your free resource kit, The Life-Changing Magic of Peptides: How the Most Important Discovery In Modern Medicine Was Hidden From the World by clicking here:
